FFLIES aims to fabricate a heterogeneously integrated BaTiO3 film optical phase modulator by μ-transfer printing BaTiO3 coupons on photonic integrated circuits (PICs). The performance of the modulator will be validated by determining the Figure of Merit (FoM) (VπLα) and compared with the current state-of-the-art in heterogeneously integrated phase modulators (VπLα < 5 V dB). Demonstration of a proof of performance of the fabricated BaTiO3 films and showing compatibility with a Back-End-of-Line (BEOL) integration method (e.g. μ-transfer printing) are vital aspects in the valorization pathway. The overall goal is to establish a spin-off company to commercialize BaTiO3... Read more
SCRiPTS research topics
|
Funding: VLAIO - Industrial Research Fund (IOF) Period: 2024 - ...
|
|
Funding: FWO-PD 1280025N Period: November 2024 - October 2027
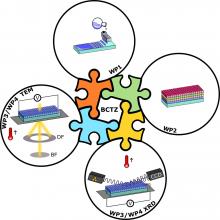
Today, the rapid evolution of information technology requires reliable microelectronic devices with excellent piezoelectric properties. The lead-free (Ba,Ca)(Ti,Zr)O3 (BCTZ) film has been developed via chemical solution deposition and pulsed laser deposition methods, which is called promising and has a high piezoelectric coefficient. Unfortunately, these BCTZ films show a poor piezoelectric thermal stability upon heating, which greatly limits their practical application. Thus, to enhance the overall performance of piezoelectric BCTZ material, several compositional and microstructural modifications are introduced in this project to improve the temperature stability in... Read more |
|
Funding: VLAIO Catalisti Period: 2023 - 2027
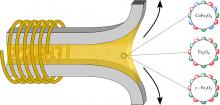
Adhesive joining is widely used in industry for its advantages over traditional fastening and welding methods. However, adhesives have drawbacks such as long curing times and difficult dismantling. To address this, magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) can be added to polymer-based adhesives, as they act as nano-heaters when exposed to an alternating magnetic field. This enables on-demand bonding and debonding. In this project, MNPs of various sizes and compositions (e.g., cobalt ferrites, magnetite, and nanoflowers) are synthesized and modified with different ligands to optimize their dispersion and interaction with the polymer.
|
|
Funding: FWO-SB 1SA4221N ; Ghent University Special Research Fund (BOF) ; Industrial Research Fund (IOF) Period: 2018 - ...
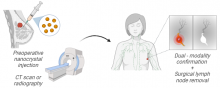
Breast cancer is the most common cancer worldwide. An important part of the surgical treatment is the removal of the so-called sentinel lymph nodes. The status of these lymph nodes, containing cancer cells or not, helps decide whether adjuvant chemo-and or radiotherapy are needed. This highly interdisciplinary research line develops and tests multimodal nanocrystals for the detection of sentinel lymph nodes using imaging techniques that are faster, more-readily available and more accurate than the current clinical standard. This project combines applied research, as well as a valorisation trajectory to bring the lead compound to clinical use for pathologies such as... Read more |
|
Funding: FWO-SB 1S11721N Period: November 2020 – October 2024
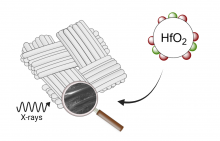
Computed tomography (CT) has revolutionized the way materials are visualized by revealing intricate internal structures which are invisible to the naked eye. However, for many materials their internal structure is virtually unattainable die to the poor CT contrast between different components. The intrinsic material properties of hafnium oxide nanocrystals make them excellent candidates for CT contrast agents. We explore their potential in contrast-enhanced polymer nanocomposites by optimizing their synthesis and surface chemistry, using them in applications such as vascular casting and fiber reinforced polymers. |
|
Funding: FWO-FR 1163125N Period: November 2022 - October 2026
Adhesive joining is increasingly preferred over mechanical joining in high-end applications, due to better stress distribution, lower weight, and the ability to join dissimilar materials. However, adhesives have lower mechanical strength compared to mechanical fasteners. To address this, nanoparticles are added as reinforcements, though the exact toughening mechanisms remain debated. This project synthesizes HfO2 nanocrystals in different sizes and with various surface chemistries to study the role of these parameters in nanoreinforced adhesives. The nanocrystals act as both tunable nano tougheners and contrast agents, enabling dynamic visualization of the... Read more |
|
Funding: FWO-SB 3S041219 Period: November 2019 - October 2023
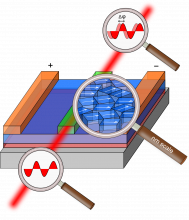
Our digital world is growing at great speed implying the constant need for improving the network quality, broadening band widths allowing fast data traffic. A vital part in these state-of-the-art optical networks is the electro-optical modulator which is much faster than the classic electrical switches. Based on the concept of tuned constructive and destructive interaction of light waves, the electro-optical modulator can act as a fast optical switch allowing fast data communication. This optical modulator are build-up of materials possessing high Pockels coefficients such as graphene, LiNbO3, Pb(Zr,Ti)O3, ... . In this project, we aim at the integration of the electro... Read more |
|
Funding: VLAIO BAEKELAND MANDATE HBC.2018.2090 Period: 2018 - 2022
Most plastic films, coatings or coated plastic films for outside applications, which are exposed to harsh sunlight, tend to degrade due to the destructive force of UV radiation. Although thin silica coatings, comparable to normal window glass, are not affected by UV radiation, they do not prevent the degradation of their substrate material. The main objective of this project is the synthesis and formulation of silica-based nanocomposite coatings with UV-absorptive/reflective properties, which can be applied on flexible plastic substrates by common industrial coating techniques, such as roll-, dip-, and spray-coating. This project is a... Read more |
|
Funding: FWO-SB 3S006418 Period: January 2018 - March 2022
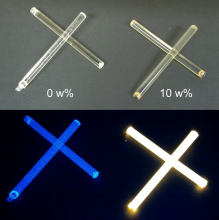
Fibre-reinforced polymers exhibit a high strength to weight ratio. Therefore, they fit in the growing trend towards more sustainable technologies, as the focus there also lies on saving energy by using lighter materials, next to the generation of electrical power using for example wind energy. However, within these composites, damage initiates very early in time and grows gradually. In this context, mechanoluminescent ZnS:Mn/ZnS core/shell nanocrystals emerge as interesting materials for continuous damage monitoring, which is key for operational reliability and human safety. We focus on simple, full yield, one-pot-synthesis of ZnS:Mn/ZnS... Read more |
|
In recent years, the need for smart window materials that lower the energy consumption for heating, venting and air-conditioning of buildings has grown immensely. These smart materials undergo a reversible change in physical properties depending on various conditions. A material that fits this description is vanadium dioxide, a thermochromic material that changes from a monoclinic to a rutile phase when heated above a critical temperature. This metal-insulator transition (MIT) leads to the absorption of infrared radiation. By absorbing this, a lower amount of heating-up occurs inside buildings and less cooling is needed. During this work, the main focus is the development of... Read more |